Strategic alliances leveraging artificial intelligence have become a cornerstone of competitive advantage. Yet, as organizations double down on AI investments—with nearly 70% of leaders planning to spend between $50-250 million on related initiatives in the coming year—a critical challenge persists: effectively measuring the return on these substantial investments while managing associated risks.
ROI Measurement Frameworks for AI Alliance Investments: Aligning with NIST AI RM
The AI landscape in 2025 is characterized by high expectations but elusive success metrics. Despite significant investments, only 31% of leaders anticipate being able to evaluate ROI within six months, and traditional methods for assessing returns struggle to capture AI’s multifaceted benefits. This is particularly true for alliance partnerships, where value creation occurs across organizational boundaries.
As I explore in Chapter 3 of my book, “AI-Powered Partnerships: Revolutionizing Alliances in The Age of GenAI,” navigating these critical challenges while identifying strategic opportunities is essential for organizations seeking to harness AI’s transformative potential. The complexity of measuring AI ROI requires sophisticated approaches that go beyond traditional metrics.
Aligning ROI Measurement with the NIST AI Risk Management Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) AI Risk Management Framework provides a valuable structure for approaching AI partnerships. Released in January 2023 and updated with a Generative AI Profile in July 2024, this framework offers a comprehensive approach to managing AI risks throughout the entire lifecycle—from development to deployment and even decommissioning.
The NIST AI Lifecycle and Key Stakeholders
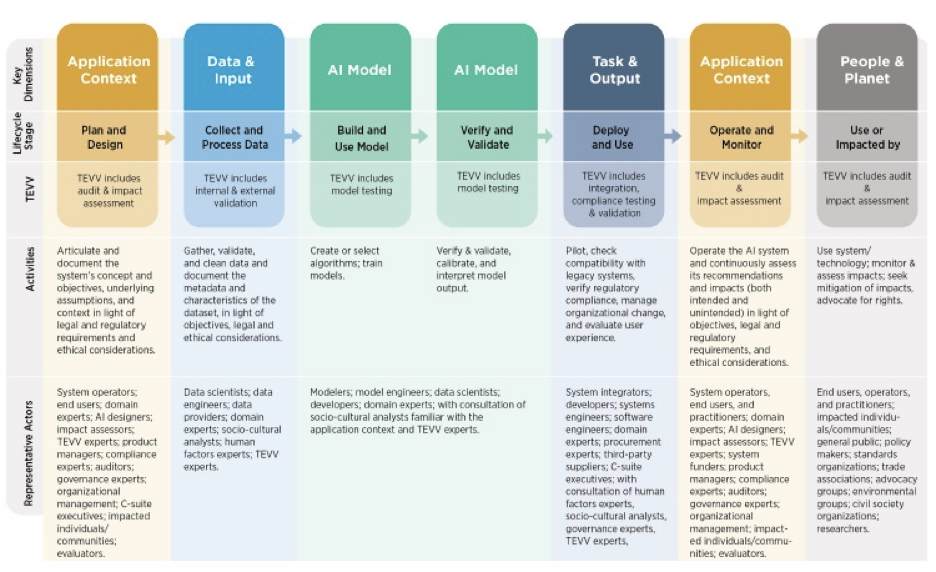
The NIST AI Framework illustrates the complete AI lifecycle stages, from application context and data input through model development and deployment to operational monitoring and impact assessment. The framework also identifies relevant stakeholders and activities at each stage.
The NIST AI RMF is structured around four core functions—Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage—which align perfectly with effective ROI measurement approaches for AI alliances. These functions provide a structured way to identify, assess, and mitigate AI risks without stifling innovation, while ensuring maximum value creation.
1. Govern: Aligning with Business Objectives and Partnership Vision
As emphasized in the NIST framework, the Govern function “cultivates and implements a culture of risk management” and “permeates each of the remaining AI RMF functions.” This parallels our approach to aligning AI partnerships with business objectives.
In Chapter 6 of “AI-Powered Partnerships,” I explore how establishing proper governance structures helps organizations:
- Define clear partnership objectives aligned with strategic goals
- Establish roles, responsibilities, and decision-making protocols
- Set up data sharing and ethics guidelines
- Create accountability frameworks for measuring success
The governance component ensures that AI investments are strategically aligned with organizational goals and that ROI measurement reflects true business value. As shown in the NIST framework diagram, this involves articulating and documenting the application context, including business objectives, underlying assumptions, and ethical considerations—essential foundations for meaningful ROI measurement.
2. Map: Identifying Value Creation Opportunities
The NIST framework’s Map function involves identifying and analyzing the context and potential impacts of AI systems. In partnership ROI measurement, this translates to mapping all potential value creation vectors:
- Financial Impact: Revenue growth, cost reduction, and margin improvement
- Operational Efficiency: Process automation, time savings, and resource optimization
- Customer Experience: Satisfaction scores, retention rates, and engagement metrics
- Innovation Potential: New offerings, market expansion, and competitive differentiation
- Partnership Value: Knowledge transfer, capability building, and ecosystem strength
As outlined in Chapter 4, “The Exponential Advantage: How GenAI Creates Shared Value,” this comprehensive mapping of value creation opportunities ensures that ROI measurement captures the full spectrum of benefits from AI partnerships.
The NIST framework highlights the importance of understanding data characteristics, model selection, and verification at this stage—all critical elements for ensuring that AI investments deliver measurable value. The framework’s emphasis on gathering, validating, and documenting data characteristics aligns with our approach to identifying value creation opportunities in AI partnerships.
3. Measure: Implementing Time-Phased Evaluation Models
The Measure function in the NIST framework involves assessing and analyzing AI risks. Similarly, thorough ROI measurement requires robust evaluation metrics and systems. Drawing from the framework, effective measurement should be:
- Comprehensive: Covering both quantitative and qualitative benefits
- Phased: Accounting for different stages of partnership maturity
- Contextual: Tailored to specific use cases and industries
- Transparent: Clear and understandable to all stakeholders
In Chapter 7, “The Partnership Imperative: Success Stories and Lessons Learned,” I provide detailed analysis of these measurement approaches across different partnership phases:
- Pre-Implementation: Establish baseline metrics and projected outcomes
- Early Adoption: Focus on capability building and initial use case validation
- Scaling Phase: Track operational improvements and initial financial returns
- Maturity Stage: Measure comprehensive business impact and strategic value
This phased approach aligns with NIST’s emphasis on continuous assessment throughout the AI lifecycle. As illustrated in the NIST diagram, measurement activities include model testing, verification, validation, and compliance testing—all crucial aspects of ensuring that AI investments deliver the expected returns.
4. Manage: Optimizing Value and Mitigating Risks
The final function in the NIST framework is Manage, which involves prioritizing and responding to risks. In the context of ROI, this translates to optimizing value creation while addressing challenges:
- Cross-Alliance Learning: Sharing best practices and insights across partnerships
- Continuous Improvement: Refining approaches based on performance data
- Risk Mitigation: Addressing data quality, bias, and other challenges that could impact ROI
- Value Optimization: Maximizing returns through strategic adjustments
As explored in Chapter 13, “Making AI Partnerships Work: Overcoming Obstacles, Maximizing Benefits,” this continuous management approach ensures that AI partnerships deliver maximum value while minimizing risks.
The NIST framework emphasizes the operational aspects of AI management, including monitoring and evaluating impacts—both intended and unintended. These activities provide crucial inputs for ROI measurement, ensuring that value assessment encompasses the full range of impacts, from financial returns to broader societal and environmental effects.
Practical Implementation Guide Aligned with NIST AI RMF
By integrating the NIST AI RMF with ROI measurement, organizations can implement a comprehensive approach to AI partnerships that balances value creation with responsible innovation.
Step 1: Define Alliance-Specific Objectives and Metrics (Govern)
This initial step establishes governance structures and defines specific, measurable goals that align with business objectives. Following the NIST framework’s emphasis on clear governance, organizations should:
- Define partnership vision and specific objectives
- Establish success metrics aligned with these objectives
- Create governance structures for oversight and accountability
- Develop ethical guidelines and data sharing protocols
The Strategic Alliance Metric Framework presented in Chapter 13 offers templates and worksheets for identifying and prioritizing these metrics within a governance context.
Step 2: Map Value Creation Opportunities (Map)
Following the NIST Map function, this step involves identifying and analyzing all potential sources of value from the partnership:
- Conduct a comprehensive assessment of potential benefits
- Identify key stakeholders and their interests
- Analyze data requirements and availability
- Assess potential risks and challenges
Chapter 8, “Building Partnership Ecosystems: Frameworks for Success,” provides frameworks for mapping value creation opportunities across different partnership types.
Step 3: Implement Measurement Systems (Measure)
Aligned with the NIST Measure function, this step involves establishing systems to track and evaluate partnership performance:
- Implement data collection and tracking systems
- Establish tiered evaluation frameworks for different partnership types
- Set up regular assessment and feedback mechanisms
- Create dashboards for real-time monitoring
Chapter 15, “Partnership Innovation: GenAI as a Transformation Catalyst,” explores how leading organizations are implementing these measurement systems to track value creation at each level of AI maturity.
Step 4: Optimize and Scale (Manage)
The final step, corresponding to the NIST Manage function, focuses on optimizing value creation and addressing challenges:
- Analyze measurement data to identify improvement opportunities
- Share best practices across partnership portfolio
- Address data quality and other technical challenges
- Scale successful models and approaches
Chapter 17, “Implementing Your GenAI Partnership Strategy,” provides practical guidance on optimizing and scaling AI partnerships based on performance data, with emphasis on continuous improvement and adaptation.
The Role of Stakeholder Engagement in ROI Measurement
The NIST framework emphasizes the importance of diverse stakeholder involvement across the AI lifecycle. As shown in the diagram, each stage requires input from different specialists, from data scientists and modelers to system operators and domain experts.
Similarly, effective ROI measurement for AI partnerships requires engagement from diverse stakeholders:
- Executive Leadership: Providing strategic direction and oversight
- Technical Teams: Offering insights on AI capabilities and limitations
- Business Units: Contributing domain expertise and operational context
- Partner Organizations: Sharing perspectives on collaborative value creation
- End Users: Providing feedback on usability and impact
This multi-stakeholder approach ensures that ROI measurement captures the full spectrum of value created by AI partnerships, from technical performance to business impact to broader societal benefits.
Conclusion
By aligning ROI measurement for AI partnerships with the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, organizations can create a holistic approach that simultaneously maximizes value and minimizes risks. This integrated framework ensures that AI investments deliver measurable returns while adhering to best practices for responsible and trusted AI development.
As AI continues to transform business operations, those alliance partners who establish robust measurement frameworks aligned with NIST guidelines will be best positioned to maximize returns and drive sustainable growth in the AI-powered future. The AI Alliance ROI Assessment Tool included in the appendix of “AI-Powered Partnerships” provides a practical starting point for organizations beginning this journey, with specific guidance on implementing NIST-aligned measurement approaches.
Align your strategy with the NIST AI RMF—because guessing ROI in 2025 is not a strategy.
